

Some of the major advantages of these methods, according to Zatorre, are the influence on stimulus on ear asymmetries can be assessed and eliminated, minimizing the attentional factors as the effect is localized to midline and percept is unitary and stimulus dominance effect may be calculated explicitly.

The main difference in this test is as such the stimuli used in this test are aligned and constructed in such a manner that partial interaural fusion occurs and subjects who take these tests generally report and experience only one stimulus per trial. In this dichotic fused words test (DFWT), each participant is exposed to the pairs of monosyllabic rhyming consonant vowel consonant (CVC) words with each word varying from the initial consonant. This test was further modified in the early 1980s by Hawles and Wexler to get more accurate data pertaining to language function of hemispheric specialization.

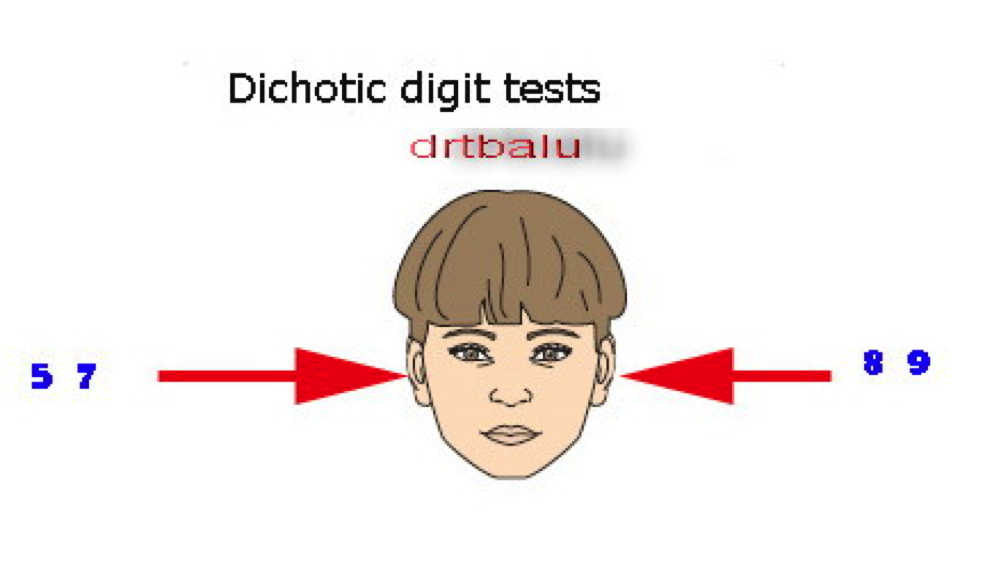
This is a modified version of the basic dichotic listening test and was put forward by Jonson in 1977. There is not just one type of listening but many. The different formants of vowel sounds are crucial still the participants were able to identify the vowel even after hearing incomplete components of the sound in different ears. He carried out studies using where participants were able to join different components of the syllable to form the one syllable even when presented to different ears. This demonstration of varying intensities in one ear with the main stimuli in the other ear was firstly known as the “Rand effect” which was later on called as “dichotic release from masking”.ĭuring the same time another researcher at Haskins Laboratories, Jim Cutting, also researched in the area of syllables using dichotic listening tests. In this study the F2 and F3 stimuli were varied in high and low intensity. In his study, the second and third stimuli:(F2) and (F3) were presented in one ear of the participants whereas the first stimuli: (F1) was presented in the opposite ear. Tim Rand, during the early 1970s, also demonstrated the dichotic perception at Haskins Laboratories. He also concluded that the results indicate the dominace of pitch discrimination for right hemisphere. If there is a dichotic listening performance advantage in one of the ears, it can also be interpreted as an enhanced processing advantage in the area of contralateral hemisphere.Īnother example of it can be the study done by Sidtis which proved that adults used to have an advantage of left-ear for a dichotic listening pitch. Using the results from this study and other studies she carried out using neurological patients with brain lesions, she deduced that there was a predominance for melodic perception of the right hemisphere and predominance of speech perception of the left hemisphere.ĭuring the period of early 1970s and later 1960s, Michael Studdert-Kennedy and Donald Shankweiler of Haskins Laboratories used the dichotic listening tests to explains the dissociation of auditory and phonetic perception is an integral part of language by finding the phonetic structure devoid of meaning and is usually processed through the left cerebral hemisphere. On the basis of her tests she demonstrated that the participants of good health have a tendency of superior reception of verbal stimuli in the right ear and perception of melodies in left ear. He also further suggested on the basis of his work that due to the limited capacity, the information processing system for human selects which stimuli channel to attend to which later on led to the derivation of the filter model of attention.ĭoreen Kimura, in the 1960s, drew conclusions about lateral asymmetry in the brain of auditory processing using dichotic listening tests. The first scientist to systematically use the dichotic listening test in his work was Donald Broadbent.ĭuring the 1950s, Broadbent asked participants in his test to either focus on one or both of the sequence of digits by employing the dichotic listening test during his studies of attention. In this article we will discuss Dichotic Listening. Here the participant is asked to focus on both of the sounds and later on are asked either about one of the stimuli or both of them in case they were not asked to ignore one of the stimuli. The general setup of a standard dichotic listening test is such that the participant taking part in the tst is presented with two different stimuli simultaneously into different ears of the participant using headphones. This test is mostly used in the field of neuroscience and cognitive psychology. The type of psychological test which is commonly used to investigate the lateralization of brain and selective attenuation within the auditory system of the brain is known as Dichotic listening.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
